OrangeChat: A Full-Stack Chat Application
Exploring the architecture and build process of OrangeChat, a real-time chat application using Socket.io.
Building Orange Chat: A Real-Time Messaging Platform with Video Calling
Orange Chat is a modern web application that combines real-time messaging with video calling capabilities. Built with React, TypeScript, and WebRTC, this project demonstrates how to create a full-featured communication platform. Let's dive into the key components that make Orange Chat work. Check out Orange Chat here
Core Features
- Authentication System
- Real-Time Messaging
- Video Calling with WebRTC
- Responsive UI with Skeleton Loading
Authentication Context

The AuthContext.tsx file provides a robust authentication system that persists across page refreshes:
// Simplified AuthContext implementation
const AuthContext = createContext<AuthContextType | undefined>(undefined);
export const AuthProvider = ({ children }) => {
const [token, setToken] = useState(localStorage.getItem("token") || null);
const [user, setUser] = useState(JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem("user") || null);
const login = (newToken: string, newUser: UserType) => {
localStorage.setItem("token", newToken);
localStorage.setItem("user", JSON.stringify(newUser));
setToken(newToken);
setUser(newUser);
};
const logout = () => {
localStorage.removeItem("token");
localStorage.removeItem("user");
setToken(null);
setUser(null);
};
// Token validation and other methods...
};
Key authentication features:
- JWT token storage in localStorage
- Automatic token validation on app load
- User data persistence
- Clean logout functionality
Message Feed Component

The MessageFeed.tsx component handles the display of chat messages with several advanced features:
// MessageFeed highlights
const MessageFeed = ({
isLoading,
messages,
selectedUser,
onSendMessage,
isFirstTimeUser,
}) => {
const { user } = useAuth();
const reversedMessages = useMemo(() => [...messages].reverse(), [messages]);
return (
<div className="message-feed-top-container">
{isFirstTimeUser ? (
<WelcomeScreen onFindFriendsClick={onFindFriendsClick} />
) : isLoading ? (
<MessageFeedSkeleton />
) : (
<>
<MessageHeader selectedUser={selectedUser} />
<div className="message-feed">
{reversedMessages.map((message) => (
<MessageBubble
key={message.id}
message={message}
isCurrentUser={message.senderId === user?.id}
/>
))}
</div>
<MessageForm onSendMessage={onSendMessage} />
</>
)}
</div>
);
};
Notable message feed features:
- Optimized rendering with
useMemo - Date separators between messages
- Different styling for sent vs received messages
- Support for image messages
- Skeleton loading states
- First-time user onboarding
Video Calling with WebRTC
The VideoCall.tsx component implements peer-to-peer video calling:
// VideoCall implementation highlights
const VideoCall = ({ otherUserId, onEndCall, isCaller, offer }) => {
const [localStream, setLocalStream] = useState<MediaStream | null>(null);
const [remoteStream, setRemoteStream] = useState<MediaStream | null>(null);
const peerConnection = useRef<RTCPeerConnection | null>(null);
const initializeCall = useCallback(async () => {
const pc = new RTCPeerConnection({
iceServers: [{ urls: "stun:stun.l.google.com:19302" }]
});
const stream = await navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia({
video: true,
audio: true
});
stream.getTracks().forEach(track => pc.addTrack(track, stream));
pc.ontrack = (event) => {
const remoteStream = new MediaStream();
event.streams[0].getTracks().forEach(track => remoteStream.addTrack(track));
setRemoteStream(remoteStream);
};
if (isCaller) {
const offer = await pc.createOffer();
await pc.setLocalDescription(offer);
emitCallOffer({ calleeId: otherUserId, offer });
} else {
await pc.setRemoteDescription(offer);
const answer = await pc.createAnswer();
await pc.setLocalDescription(answer);
answerVideoCall(otherUserId, answer);
}
}, [isCaller, otherUserId, offer]);
// Call controls
const toggleMute = () => {
localStream?.getAudioTracks().forEach(track => track.enabled = !track.enabled);
};
const toggleVideo = () => {
localStream?.getVideoTracks().forEach(track => track.enabled = !track.enabled);
};
});
Video calling features:
- WebRTC peer connection management
- STUN server configuration for NAT traversal
- Media stream handling
- Caller/callee role differentiation
- Mute and video toggle controls
- Connection status monitoring
Find Friends Feature
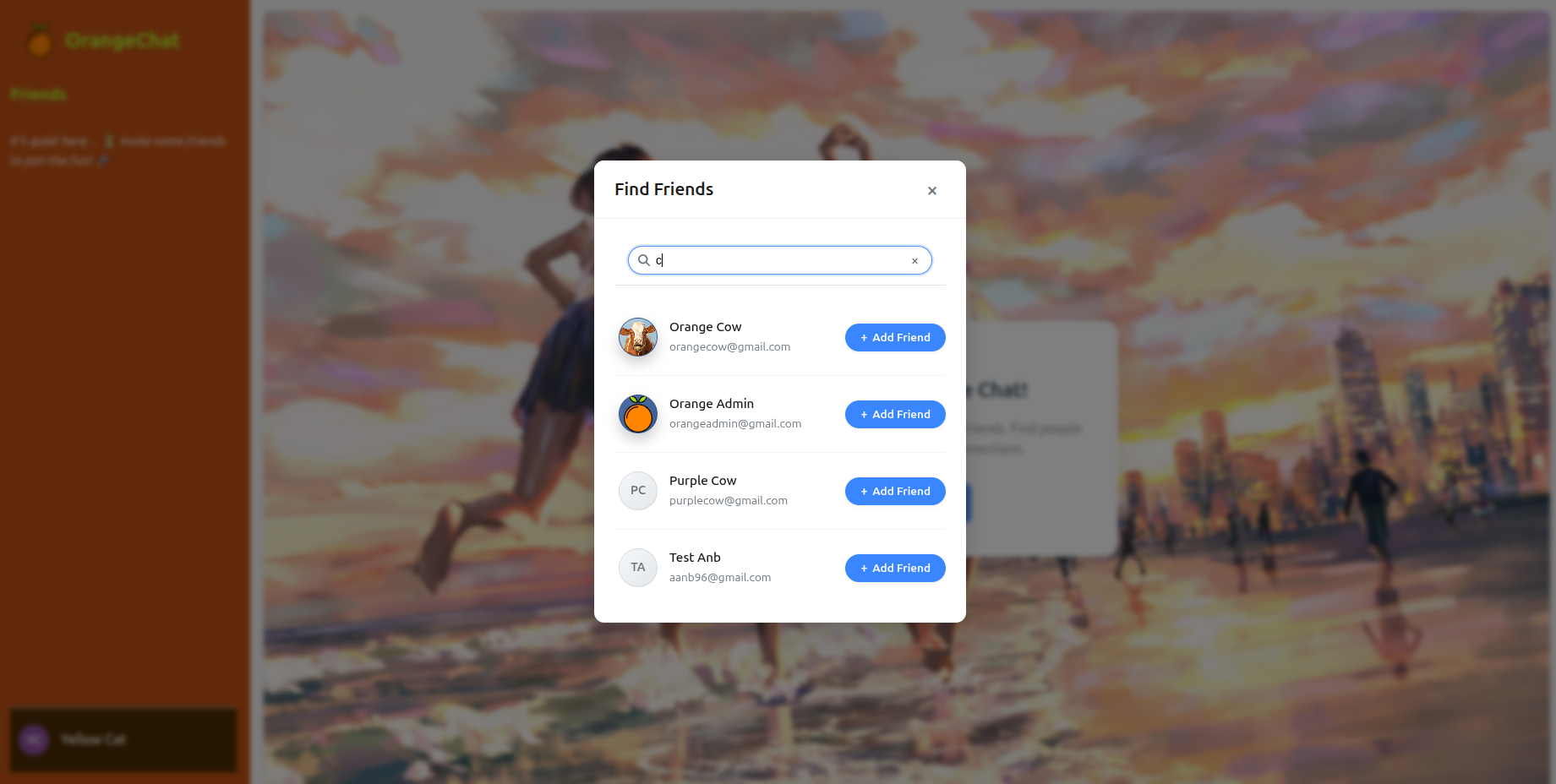
The FindFriendsModal.tsx component provides a user-friendly interface for discovering and connecting with other users. This feature demonstrates several important patterns in React development:
// Key aspects of the FindFriendsModal implementation
const FindFriendsModal = ({
isOpen,
onClose,
onSearch,
searchResults,
onAddFriend,
searchQuery,
}) => {
// Component implementation...
};
Key features of the Find Friends system:
-
Search Functionality:
- Real-time user search with debouncing
- Search by name or email address
- Clean UI with loading states
-
Friendship Status Management:
- Visual indicators for different friendship states (pending, accepted, rejected)
- Disabled buttons for existing relationships
- Custom icons for each status
-
User Display:
- Profile images with fallback to initials
- Clean layout showing name and email
- Responsive design for all screen sizes
-
Modal Behavior:
- Controlled open/close state
- Overlay click detection
- Keyboard accessibility
The friendship status system is particularly noteworthy, as it handles multiple states through a centralized button configuration:
const getButtonState = (status?: string) => {
switch (status) {
case "accepted":
return {
text: "Friends",
className: "friend-button friends",
disabled: true,
};
case "pending":
return {
text: "Pending",
className: "friend-button pending",
disabled: true,
};
// ... other cases
}
};
This pattern keeps the UI consistent while allowing for easy expansion of additional friendship states.
Express Server Architecture
The backend of OrangeChat is built with Express.js, providing a robust API layer for the application. The server setup in index.ts demonstrates several production-ready patterns:
// Generalized server configuration
const app = express();
// Essential middleware
app.use(
cors({
origin:
process.env.NODE_ENV === "production"
? [process.env.PROD_ORIGIN]
: [process.env.DEV_ORIGIN],
credentials: true,
})
);
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.use(cookieParser());
// Modular route organization
app.use("/auth", authRoutes);
app.use("/api", apiRoutes);
// Production handling (static files and client-side routing)
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === "production") {
app.use(express.static("client-build"));
app.get("*", (req, res) => res.sendFile("client-build/index.html"));
}
// WebSocket integration through shared HTTP server
const server = http.createServer(app);
initWebSocket(server);
Key server features:
-
Middleware Configuration:
- CORS with environment-specific origins
- JSON body parsing
- Cookie parsing for authentication
- Static file serving in production
-
Route Organization:
- Modular route handlers (login, home, friends)
- Separation of concerns between different feature areas
- Clean import structure
-
Production Considerations:
- Environment variable configuration
- Frontend asset serving in production mode
- Catch-all route for client-side routing
-
WebSocket Integration:
- Shared HTTP/WebSocket server
- Clean initialization pattern
- Support for both REST and real-time communication
The server architecture supports both development and production environments, with special handling for static assets in production:
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === "production") {
app.use(express.static("client-build"));
app.get("*", (req, res) => res.sendFile("client-build/index.html"));
}
This setup ensures the React frontend is properly served in production while maintaining API routes for backend functionality.
Conclusion
Orange Chat demonstrates several modern web development techniques:
- Context API for state management
- WebRTC for real-time communication
- Optimized rendering with React hooks
- Responsive UI with loading states
- Secure authentication flow
The combination of these technologies creates a seamless user experience for both messaging and video calling. Future enhancements could include group calling, message reactions, and end-to-end encryption.